A Processor Contains Thirty-two 16-bit Registers. How Many Flip Flops Are Required ?
Flip flops can be used to store a unmarried bit of binary information (1or 0). Nonetheless, in order to store multiple $.25 of data, we need multiple flip flops. North flip flops are to exist connected in an society to store n $.25 of data. A Annals is a device which is used to store such information. It is a group of flip flops continued in serial used to store multiple $.25 of data.
The information stored inside these registers can be transferred with the help of shift registers. Shift Register is a group of flip flops used to shop multiple bits of data. The bits stored in such registers can be fabricated to movement within the registers and in/out of the registers by applying clock pulses. An north-flake shift annals can be formed past connecting due north flip-flops where each flip bomb stores a single fleck of data.
The registers which volition shift the bits to left are chosen "Shift left registers".
The registers which will shift the bits to correct are chosen "Shift right registers".
Shift registers are basically of 4 types. These are:
- Serial In Serial Out shift register
- Serial In parallel Out shift register
- Parallel In Serial Out shift register
- Parallel In parallel Out shift register
Serial-In Serial-Out Shift Register (SISO) –
The shift annals, which allows serial input (one bit after the other through a single data line) and produces a serial output is known as Serial-In Serial-Out shift annals. Since there is only one output, the data leaves the shift annals one bit at a time in a serial pattern, thus the name Serial-In Series-Out Shift Register.
The logic circuit given beneath shows a series-in serial-out shift register. The excursion consists of iv D flip-flops which are connected in a serial fashion. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since the same clock indicate is practical to each flip flop.

The above circuit is an example of shift correct annals, taking the serial data input from the left side of the flip bomb. The main employ of a SISO is to human activity equally a filibuster chemical element.
Series-In Parallel-Out shift Register (SIPO) –
The shift register, which allows serial input (1 fleck later on the other through a single data line) and produces a parallel output is known as Series-In Parallel-Out shift register.
The logic excursion given below shows a serial-in-parallel-out shift register. The excursion consists of four D flip-flops which are connected. The clear (CLR) signal is connected in addition to the clock betoken to all the iv flip flops in order to RESET them. The output of the showtime flip bomb is continued to the input of the next flip flop and and then on. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since the same clock bespeak is applied to each flip flop.

The above circuit is an example of shift right register, taking the serial data input from the left side of the flip flop and producing a parallel output. They are used in communication lines where demultiplexing of a data line into several parallel lines is required because the primary use of the SIPO annals is to convert serial information into parallel information.
Parallel-In Series-Out Shift Register (PISO) –
The shift register, which allows parallel input (information is given separately to each flip flop and in a simultaneous manner) and produces a series output is known as Parallel-In Serial-Out shift annals.
The logic circuit given beneath shows a parallel-in-series-out shift register. The circuit consists of four D flip-flops which are connected. The clock input is direct connected to all the flip flops just the input data is continued individually to each flip flop through a multiplexer at the input of every flip bomb. The output of the previous flip flop and parallel information input are continued to the input of the MUX and the output of MUX is connected to the next flip flop. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since the same clock point is applied to each flip flop.

A Parallel in Serial out (PISO) shift register us used to catechumen parallel data to serial data.
Parallel-In Parallel-Out Shift Register (PIPO) –
The shift register, which allows parallel input (data is given separately to each flip flop and in a simultaneous manner) and also produces a parallel output is known equally Parallel-In parallel-Out shift register.
The logic circuit given beneath shows a parallel-in-parallel-out shift register. The circuit consists of four D flip-flops which are connected. The clear (CLR) signal and clock signals are connected to all the four flip flops. In this type of register, there are no interconnections betwixt the private flip-flops since no serial shifting of the data is required. Data is given as input separately for each flip flop and in the same way, output also collected individually from each flip flop.

A Parallel in Parallel out (PIPO) shift register is used equally a temporary storage device and like SISO Shift register it acts as a delay element.
Bidirectional Shift Register –
If we shift a binary number to the left past one position, information technology is equivalent to multiplying the number by 2 and if nosotros shift a binary number to the right by one position, information technology is equivalent to dividing the number by 2.To perform these operations nosotros demand a register which tin shift the information in either management.
Bidirectional shift registers are the registers which are capable of shifting the data either correct or left depending on the mode selected. If the mode selected is ane(loftier), the data will be shifted towards the right direction and if the mode selected is 0(low), the data volition exist shifted towards the left direction.
The logic circuit given beneath shows a Bidirectional shift register. The excursion consists of four D flip-flops which are connected. The input data is connected at two ends of the circuit and depending on the mode selected only 1 and gate is in the active state.

Shift Register Counter –
Shift Register Counters are the shift registers in which the outputs are continued dorsum to the inputs in order to produce particular sequences. These are basically of 2 types:
- Band Counter –
A ring counter is basically a shift register counter in which the output of the first flip flop is continued to the next flip flop and so on and the output of the last flip flop is once again fed dorsum to the input of the outset flip flop, thus the proper name ring counter. The data blueprint within the shift register will circulate as long as clock pulses are applied.
The logic circuit given below shows a Ring Counter. The circuit consists of four D flip-flops which are connected. Since the circuit consists of four flip flops the data blueprint will repeat later on every four clock pulses as shown in the truth table below:


A Ring counter is by and large used because information technology is cocky-decoding. No actress decoding circuit is needed to make up one's mind what state the counter is in.
- Johnson Counter –
A Johnson counter is basically a shift register counter in which the output of the first flip flop is continued to the side by side flip flop and then on and the inverted output of the last flip flop is again fed back to the input of the first flip flop. They are also known as twisted band counters.The logic excursion given beneath shows a Johnson Counter. The circuit consists of four D flip-flops which are connected. An n-stage Johnson counter yields a count sequence of 2n different states, thus too known as a modernistic-2n counter. Since the circuit consists of iv flip flops the data design volition repeat every viii clock pulses as shown in the truth tabular array beneath:

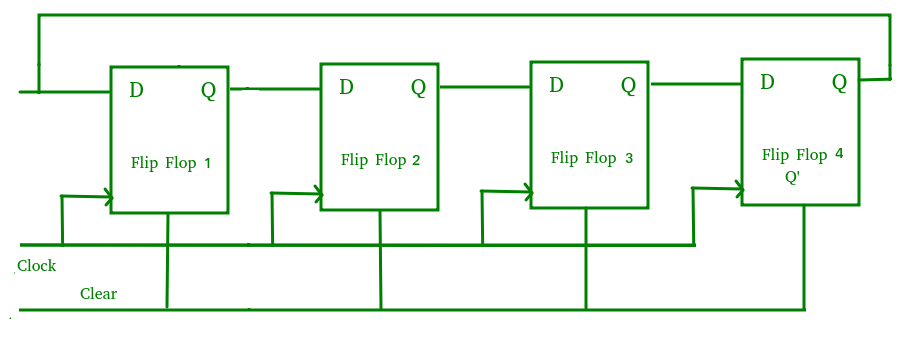
The main advantage of Johnson counter is that it but needs north number of flip-flops compared to the band counter to circulate a given data to generate a sequence of 2n states.
Applications of shift Registers –
- The shift registers are used for temporary data storage.
- The shift registers are also used for information transfer and information manipulation.
- The series-in serial-out and parallel-in parallel-out shift registers are used to produce time filibuster to digital circuits.
- The serial-in parallel-out shift register is used to convert serial information into parallel information thus they are used in communication lines where demultiplexing of a information line into several parallel line is required.
- A Parallel in Serial out shift annals us used to convert parallel information to serial data.
Reference –
Registers – ee.usyd.edu.au
A Processor Contains Thirty-two 16-bit Registers. How Many Flip Flops Are Required ?,
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/shift-registers-in-digital-logic/
Posted by: molinaplacre1982.blogspot.com


0 Response to "A Processor Contains Thirty-two 16-bit Registers. How Many Flip Flops Are Required ?"
Post a Comment